Recuperative thermal oxidation
- Recuperative thermal oxidation is a process based on direct after-burning of organic and inorganic pollutants in the waste gas.
- Our devices are suitable for the processing of 1.000 to 25.000 Nm3 of waste gas per hour.
- The trade name of the device is TNV EVR.
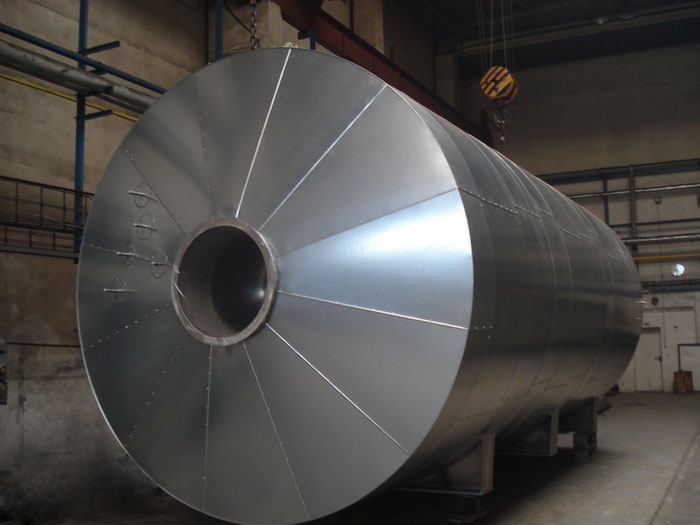
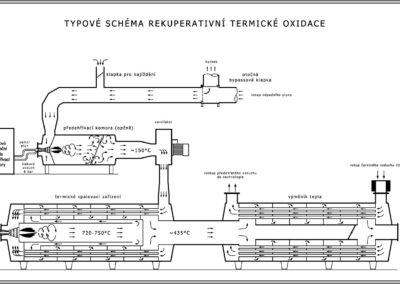
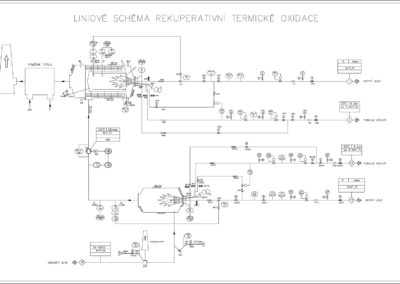
- EVR is a thermal oxidizer used for cleaning of the waste gas. It has a compact construction with an integrated system of recuperative heat recovery. The oxidizer oxidizes organic compounds in the waste gas. The inorganic compounds are either oxidized or converted into more stable compounds.
The oxidizer consists of one central steel combustion chamber, a burner and a heat-exchanger with a circular bundle of pipes.
The waste gas containing the pollutants is taken in by a fan and let to the combustion chamber. To save fuel, the gas is first preheated in an inbuilt heat exchanger and then it is heated by a gas burner to the temperature necessary for the reaction. The oxidation of the pollutants takes place at the temperature of 650 to 750°C. The cleaned gas is then pushed through the heat-exchanger where it returns a large portion of its energy to the uncleaned waste gas.
The combustion chamber is big enough to guarantee that waste gas spends enough time there for the pollutants to be oxidized while the flame is not visible.
The cleaned gas contains mostly O2, N2, CO2, a H2O and it can be let out into the atmosphere without any further processing.
The oxidizer can only be installed in an environment with no explosion hazard. The regulation system must be able to guarantee that the concentration of the organic carbon does not exceed 20% of the lower explosive limit (LEL).
These devices can be used in the car, textile, polygraphic, chemical and other industry. They are suitable both for continuous and non-continuous operation.